Q&A With UAB Med School Dean Selwyn Vickers: Pandemic “Significantly” Shutting Down Clinical Trial Enterprise
By Hank Black
Dr. Selwyn Vickers, UAB senior vice-president and dean of the School of Medicine, is a busy person as he deals with the COVID-19 pandemic. But BirminghamWatch caught a few minutes with him Thursday to ask a quick series of questions.
BW: Are there shortages of equipment and fluids for kidney dialysis or of ventilator medicines such as sedatives, anesthetics, painkillers and muscle relaxants? That’s happening in some parts of the country.
Vickers: We have no shortages for kidney dialysis. As for ventilator meds, we’re lower than usual, but I don’t think we’re in a dangerous position. This (pandemic) has taxed our supply but hasn’t necessarily put us in an at-risk position. Our supply is lower than it used to be, no doubt because we’ve had so many patients on ventilators. We are seeing a gradual decrease in the number of patients in the hospital on ventilators, and of those being discharged from the hospital, so we are at least maintaining our supply and hopefully keeping it from being further decremented.
BW: Have you seen a decrease in cases of asthma attacks and other respiratory conditions due to the cleaner air we’re experiencing in the city?
Vickers: Actually, we’ve seen a downturn in all diseases. Cancer patient care and renal dialysis is still going on, but the hospital is only about half full, and our clinics are not fully operating except for telemedicine.
BW: How is COVID-19 and orders to shelter at home affecting research at UAB?
Vickers: Other than those clinical trials that are for cancer therapy – patients getting novel or early development drugs for a cancer that doesn’t have any other treatment – the virus has significantly shut them down. It’s temporarily closed many of the trials under the current conditions.
Some are able to work from home to carry out some activities, but a lot of the workers who do the work accruing participants don’t have anything to do now. That’s a problem. It’s affecting our bottom line in a very significant way, since more than half the trials are not running. The trials that are running are largely where there’s cancer care without other options.
The overall business of performing procedures, seeing in clinics, and admitting to the hospital – all those are down due to COVID-19.
BW: When this pandemic started, was there consideration of what role Cooper Green Mercy Hospital might play?
Vickers: Yes, I think early on there were thoughts given to using Cooper Green, but all the latest modeling shows we have a significant excess of beds, ICU beds and ventilators both in the state and at UAB.
BW: What’s the future look like for the medical enterprise?
Vickers: Early on, we started a parallel process to begin asking how we would be different and better from all this. There are legitimately some things no longer done that we won’t do again. And there are some things we have learned to do and would only have been able to do in a crisis that will probably continue and will be a new normal for us. It’s an ongoing process for us to think about because of the crisis – what are the things we’re going to learn and how we’re going to be stronger due to the crisis – the one most commonly thought about is telemedicine. We were gradually doing telemedicine, but we’re doing it at a fairly massive level now, so that will certainly make our world very different.
We have a couple of task forces looking at the clinical lessons learned and at transformation opportunities, and at the broader academic side, which includes some clinical areas, but research and education as well.
BW: What about working at home?
Vickers: Some parts of the institution may create more flexibility to actually work from home. Clearly, there are certain areas that are productive and may be more productive from home. That’ll be an iterative process. I don’t know that globally there will be a greater number working from home, but I could see that this experience would get unit supervisors to entertain more requests (from employees) to work from home.
Certainly that may be the case for a period of time, because we see even as we return back to normal activities that we’re not going to want to put everybody back together again. We will want to keep (our workforce) low-density, with distance around most people.
BW: Do you see that there might be a need for reallocation of space due to working from home?
Vickers: No doubt that’s a possibility, though not for research, because that has to be done hands-on. But for some administrative functions, this may give us the ability to repurpose space.
BW: What is the status of medical residents and medical students?
Vickers: Right now we’re still expecting to start the new class of residents in July. Match Day already occurred, so they’re signed on. Current residents are busy, but not overwhelmed. We limit their engagement with COVID-10 patients, and there is some limit on didactic teaching.
As for med students, our accrediting body has asked us to keep them out of the clinical environment until it’s (safe) to go back into patient care.
BW: What’s next?
Vickers: The next big thing is seeing how we will structure to re-open and gradually remodel our world – and remind people it will not be the world as they knew it!
Birmingham is 3rd worst in the Southeast for ozone pollution, new report says
The American Lung Association's "State of the Air" report shows some metro areas in the Gulf States continue to have poor air quality.
Why haven’t Kansas and Alabama — among other holdouts — expanded access to Medicaid?
Only 10 states have not joined the federal program that expands Medicaid to people who are still in the "coverage gap" for health care
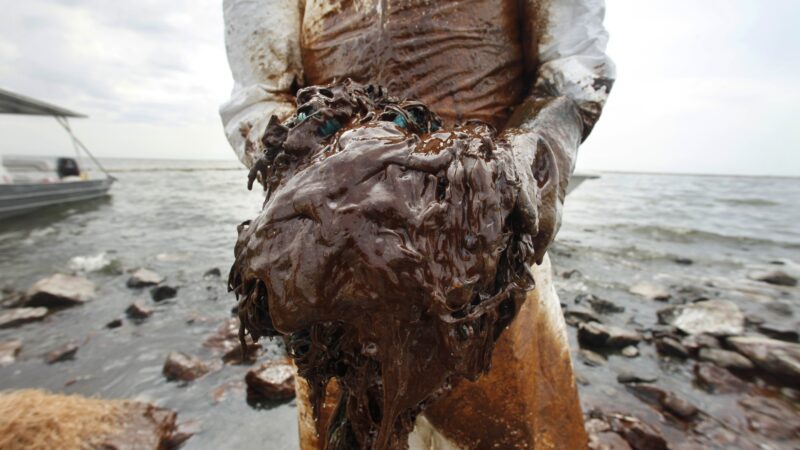
Once praised, settlement to help sickened BP oil spill workers leaves most with nearly nothing
Thousands of ordinary people who helped clean up after the 2010 BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico say they got sick. A court settlement was supposed to help compensate them, but it hasn’t turned out as expected.
Q&A: How harm reduction can help mitigate the opioid crisis
Maia Szalavitz discusses harm reduction's effectiveness against drug addiction, how punitive policies can hurt people who need pain medication and more.
The Gulf States Newsroom is hiring a Community Engagement Producer
The Gulf States Newsroom is seeking a curious, creative and collaborative professional to work with our regional team to build up engaged journalism efforts.
Gambling bills face uncertain future in the Alabama legislature
This year looked to be different for lottery and gambling legislation, which has fallen short for years in the Alabama legislature. But this week, with only a handful of meeting days left, competing House and Senate proposals were sent to a conference committee to work out differences.