UAB Using Whole Blood to Improve Trauma Care
When someone is experiencing severe blood loss, that blood needs to be replaced as soon as possible. Most doctors deliver this transfusion as a “balanced resuscitation,” combining equal amounts of red blood cells, plasma and platelets, which is how blood is separated and delivered to most U.S. hospitals. But a balanced resuscitation is not the same thing as using whole blood that has never been separated, according to Dr. Marisa Marques, medical director of transfusion services at UAB Hospital.
“You’re not able to reconstitute whole blood just mixing the other components,” Marques says, “because each one of them is somewhat diluted with anticoagulant and other substances.”
Most of the research on whole blood transfusions comes from the military and treating injured soldiers in war zones. It suggests that transfusing actual whole blood to care for hemorrhaging patients can lead to better outcomes. Patients may require less blood to be transfused, and they often recover faster. UAB trauma surgeon Dr. Daniel Cox says another advantage of using whole blood, rather than separated components, is that it saves time.
“For the very seriously injured patient, this has the potential to significantly improve the chances of that person surviving,” says Cox.
UAB Hospital recently joined a growing number of hospitals across the country that use whole blood to treat severe trauma patients. Dr. Marques says finding a supply was not easy. It is not available from the local American Red Cross (ARC), where UAB gets most of its blood products. The hospital ended up having to get it from an ARC blood bank in Oklahoma.
Marques says whole blood has to meet strict requirements. To ensure that the product can be used for most patients, she says donors have to be male with low-antigen, type O blood. And timing is key, as whole blood has a shelf life of about three weeks, which is about half that of packed red blood cells.
UAB receives 12 units every week, which is less than 5% of the hospital’s total blood supply. UAB trauma doctors say that since they started receiving the whole blood in August they have used just about every drop.
Birmingham is 3rd worst in the Southeast for ozone pollution, new report says
The American Lung Association's "State of the Air" report shows some metro areas in the Gulf States continue to have poor air quality.
Why haven’t Kansas and Alabama — among other holdouts — expanded access to Medicaid?
Only 10 states have not joined the federal program that expands Medicaid to people who are still in the "coverage gap" for health care
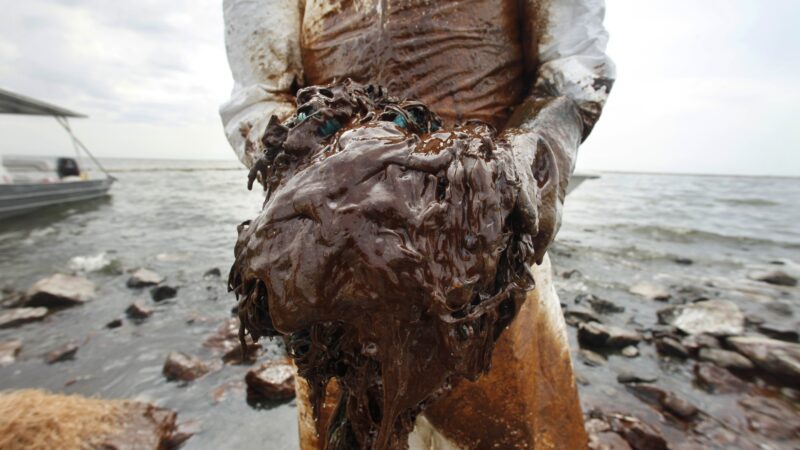
Once praised, settlement to help sickened BP oil spill workers leaves most with nearly nothing
Thousands of ordinary people who helped clean up after the 2010 BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico say they got sick. A court settlement was supposed to help compensate them, but it hasn’t turned out as expected.
Q&A: How harm reduction can help mitigate the opioid crisis
Maia Szalavitz discusses harm reduction's effectiveness against drug addiction, how punitive policies can hurt people who need pain medication and more.
The Gulf States Newsroom is hiring a Community Engagement Producer
The Gulf States Newsroom is seeking a curious, creative and collaborative professional to work with our regional team to build up engaged journalism efforts.
Gambling bills face uncertain future in the Alabama legislature
This year looked to be different for lottery and gambling legislation, which has fallen short for years in the Alabama legislature. But this week, with only a handful of meeting days left, competing House and Senate proposals were sent to a conference committee to work out differences.