Climate Change Analysis Predicts Losses for South
Scientists and economists have put together a detailed new analysis of potential economic damage from climate change in the United States. The study, published in the journal “Science,” uses decades of data to make predictions down to the county level. One takeaway: Alabama and the rest of the South could suffer more than other parts of the country. Higher energy bills, crop failures, and heat strokes are just some of the factors that will hurt economies across the South, according to the study.
The University of California at Berkeley’s James Rising, who co-authored the report, says, “Alabama stands to lose about three times the national average in its income, and that’s mostly driven by big increases in death rates.”
That can include mortality from heatwaves and associated diseases and accidents. The study predicts climate-change-related deaths in Alabama will roughly double those from car accidents by the end of the century. It also forecasts that the wealth gap between North and South will widen.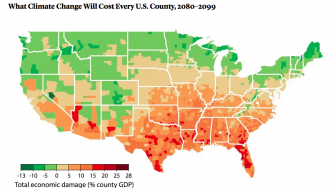
“What we find is that climate change is going to exacerbate inequality,” says Rising, “both because the South is already hotter and poorer, and because the North is actually going to, in some areas, get benefits from milder winters.”
But in Alabama, addressing climate change is not a political priority.
John Christy, Alabama’s State Climatologist, explains to companies thinking about moving to Alabama how the local climate can work to their advantage. And he says the study is just wrong.
“Climate models just aren’t reliable in terms of telling us about what’s going on now and what’s going on in the future,” he says. “The evidence for a disastrously changing climate is pretty thin.”
One thing Christy and the study authors agree on is the need to be prepared for hot and extreme weather. James Rising says there are many ways to do that. “Cities can paint the tops of their buildings white. They can plant more green spaces, make sure that they have plenty of water and air conditioning. And farmers can make sure that they invest in irrigation,” he says.
Rising says the new study is meant to help businesses, government, and other institutions better assess climate risks and make “more rational policies … We’re not trying to describe some kind of catastrophe that’s going to at some point just ‘click on.’ Climate change is going to become progressively more and more damaging and going to impact more more people, and having in hand the kind of kind of understanding that lets you choose as a society how much you’re willing to lose can really help make for better policy making.”
Q&A: How harm reduction can help mitigate the opioid crisis
Maia Szalavitz discusses harm reduction's effectiveness against drug addiction, how punitive policies can hurt people who need pain medication and more.
The Gulf States Newsroom is hiring a Community Engagement Producer
The Gulf States Newsroom is seeking a curious, creative and collaborative professional to work with our regional team to build up engaged journalism efforts.
Gambling bills face uncertain future in the Alabama legislature
This year looked to be different for lottery and gambling legislation, which has fallen short for years in the Alabama legislature. But this week, with only a handful of meeting days left, competing House and Senate proposals were sent to a conference committee to work out differences.
Alabama’s racial, ethnic health disparities are ‘more severe’ than other states, report says
Data from the Commonwealth Fund show that the quality of care people receive and their health outcomes worsened because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
What’s your favorite thing about Alabama?
That's the question we put to those at our recent News and Brews community pop-ups at Hop City and Saturn in Birmingham.
Q&A: A former New Orleans police chief says it’s time the U.S. changes its marijuana policy
Ronal Serpas is one of 32 law enforcement leaders who signed a letter sent to President Biden in support of moving marijuana to a Schedule III drug.